Literature

Native American Literature in Louisiana
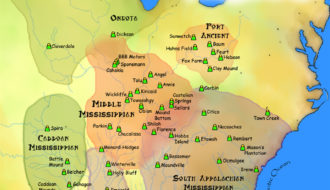
Native American culture has influenced Louisiana for at least six thousand years. Today, Louisiana is home to four federally-recognized tribes: Chitimacha, Tunica-Biloxi, Coushatta, and the Jena Band of Choctaw.