Archaeology
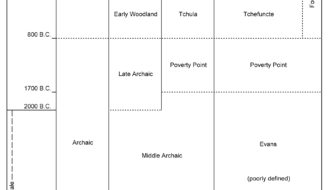
Prehistoric Archaeology in Louisiana
This entry explores the history of American Indian life in Louisiana from 11,500 BCE to 1700 CE through the study of prehistoric archaeology.

This entry explores the history of American Indian life in Louisiana from 11,500 BCE to 1700 CE through the study of prehistoric archaeology.

The Progressive movement that swept across the United States at the turn of the twentieth century brought changes to many of the nation's social and political institutions, including those in Louisiana.

Louisiana reluctantly became subject to prohibition, the effort to eliminate alcoholic drinks, as a result of the 1920 federal law commonly known as the Volstead Act.

Several Protestant denominations are present in Louisiana with Southern Baptist and Methodist as the most dominant.

The Public Works Administration projects in Louisiana during the Great Depression include numerous courthouses, university buildings, and Charity Hospital in New Orleans.

A receiving community is a city, town, or neighborhood that accommodates people displaced by a disaster.

The post-Civil War period in US history is known as the Reconstruction era, when the former Confederacy was brought back into the Union.

The post-Civil War period is known as the Reconstruction era, when the former Confederacy was brought back into the Union.

French explorer Rene-Robert Cavelier, sieur de La Salle, is perhaps best known for giving the region and ultimately the state its name: Louisiana.

Democrat Robert Wickliffe, who served as the governor of Louisiana from 1856 until 1860, oversaw the state in the increasingly tumultuous years before the Civil War.

Rock music in Louisiana grew out of several genres of roots music: blues, rhythm and blues, Cajun, and zydeco.

Rockabilly is a genre of music that derived from early rock 'n' roll, with a country-music flavor.
One-Year Subscription (4 issues) : $25.00
Two-Year Subscription (8 issues) : $40.00
