History

Unionism in Louisiana
Contrary to conventional assumptions, many Louisianans opposed secession and the Confederacy during the Civil War.

Contrary to conventional assumptions, many Louisianans opposed secession and the Confederacy during the Civil War.

Five thousand to ten thousand white Louisianans fought for the Union during the Civil War.

The act of arson at the Up Stairs Lounge, a gay bar in the French Quarter, was the deadliest fire on record in New Orleans history and the largest mass killing of queer citizens in twentieth-century America.

Enslaved people in Louisiana’s cities were engaged in virtually every labor role, from domestic service to dentistry.

Valcour Aime employed the latest technologies and oversaw the creation of an elaborate garden on his sugar plantation.

The war in Vietnam polarized the people of Louisiana just as it polarized people across the country.

Vietnamese Americans are one of the newest major ethnic groups in Louisiana
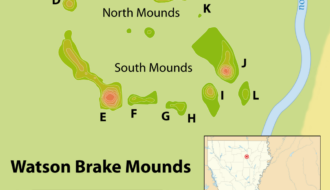
Watson Brake is a prehistoric Evans culture site in Ouachita Parish dating to 3500–2800 BCE.

One of the first Black Protestant churches in Louisiana, Wesley Chapel played pivotal roles in social and political movements, from teaching freed Black women to read after the Civil War to engaging in the civil rights movement.

The Florida Parishes were not included in the Louisiana Purchase but were under Spanish control.

A paramilitary organization aligned with the Democratic Party, the White League played a central role in the overthrow of Republican rule and intimidation of African Americans in Louisiana during Reconstruction.

Bill Russell was one of the most prominent figures in the study and documentation of traditional New Orleans jazz.
One-Year Subscription (4 issues) : $25.00
Two-Year Subscription (8 issues) : $40.00
